What is ISO 9001 Certification? 2023 Update
Small business success hangs on one major factor – customer and client trust. The ISO 9001 Standard for Quality helps organizations create, implement, and maintain a high-functioning Quality Management System (QMS) that guides the day-to-day function of the business.
An ISO QMS helps companies constantly refine their day-to-day systems and create targeted long-term goals for success. Led by the stringent quality requirements of the standard, QMS in turn helps guide the ultimate achievement of business growth – constantly improving customer experiences and satisfaction.
Through ten clauses, the ISO standard guides companies toward improved internal function and cultural growth. This document covers the basic definition of ISO 9001 as well as the basics regarding the requirements and steps to certification.
Introduction to the ISO 9001 Standard
What is ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 is a global quality standard focused on defining minimum best practices for the production and delivery of a company’s goods and/or services. It focuses on efficiency, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement, and guides organizations to the development of a formal quality management system (QMS). The QMS comprises processes and documentation that control operations and ensure that requirements are met.
Who Wrote it?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is made up of national standard bodies from more than 160 countries.
Who Uses it?
ISO 9001 can be implemented by any company of any size. Currently, there are more than a million organizations worldwide that are certified to the standard.
What are the Benefits?
Achieving certification to the ISO 9001 standard offers organizations many benefits, including the ability to constantly and consistently improve their processes, refine their deliverable, and grow their business.
Who Issues the Certificate?
A third-party registrar issues ISO 9001 certificates after an extensive audit of a company’s QMS. During the audit, they will evaluate compliance with the standard’s requirements. Surveillance audits must be repeated on an annual basis to maintain certification.
Who Needs to be Involved?
For truly successful ISO success, all members of the organization should be involved in the implementation of the new QMS.
Certification to ISO 9001 is achievable by any organization, regardless of industry or size. The internal team can implement the process, but some companies choose to utilize outside consulting resources to ensure they can appropriately translate the standard’s requirements to their business.
Is This the Only Certification?
ISO 9001 is the baseline standard that can catapult organizations into excellence in safety, environmental sustainability, information security, and more. By first certifying to the original quality standard (9001), companies position themselves for success through further standard pursuit and certification.
What Requirements are Included?
ISO 9001 requirements are organized into the following sections:
-
- Context of the Organization
- Leadership
- Planning
- Support
- Operation
- Performance Evaluation
- Improvement

Together, these requirements make up the Quality Management System (QMS) described in company documentation and include the quality manual, procedures, work instructions, records, and other information used for day-to-day operational excellence. An effective QMS is one where a company follows its processes and documentation consistently, achieves the desired results of its objectives and key performance indicators, and continually improves to perform better for its customers.
What is the Process Approach?
The ISO 9001 standard employs the Process Approach or how the processes and activities in a company work together to deliver quality products and/or services.
By examining and improving key business processes, organizations can directly impact how they serve their customer. By improving the way procedures are done, they are also able to improve the overall quality of their deliverable.
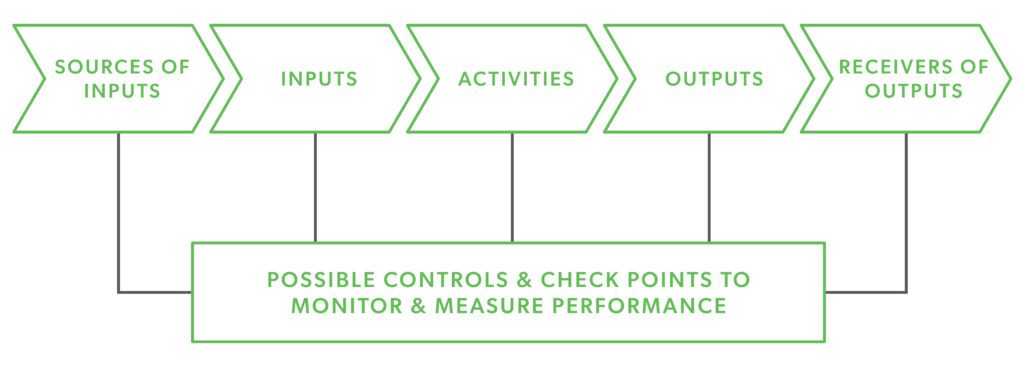
During the ISO 9001 certification process, you will evaluate and monitor six possible controls and checkpoints:
- Source of Inputs – the processes and policies of those who impact inputs
- Inputs – the physical materials, information, or resources acquired to produce products and/or services
- Activities – actions performed in the creation of goods and services
- Outputs – the quality of the final deliverable
- Receivers of Outputs – the processes of the businesses or individuals that use the final product or service
Hinging on the PDCA cycle (Plan, Do, Check, Act), the implementation of process improvements must be thoroughly thought through, documented, and monitored for continued success.
What’s Required?
“… the systematic definition and management of processes, and their interactions, to achieve the intended results by the quality policy and strategic direction of the organization. Management of the processes and the system as a whole can be achieved using the PDCA cycle (see 0.3.2) with an overall focus on risk-based thinking (see 0.3.3) aimed at taking advantage of opportunities and preventing undesirable results.” (0.3.1)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
- A process is a set of work steps that transform parts, materials, or information (inputs) into a more complete form, such as assemblies, products, or reports with outputs based on specific requirements.
- The output of one process can be the input of another process. All of your company’s processes interact and affect the final result.
- Each process is assigned a process owner who is responsible for monitoring performance objectives and KPIs and for leading the improvement of the process.
-
-
What is Operational Risk Management?
Risk-based thinking is the driving factor of decisions made by organizations working to implement an ISO 9001 QMS. By identifying potential risks and rewards, the approach helps to shape the culture of the organization into one focused on proactive processes designed to mitigate potential risks and capitalize on improvements for reward.
A formal and documented risk management process is required for ISO 9001 certification.
What are the ISO 9001:2015 Risk-Based Thinking Requirements?
“To conform to the requirements of this International Standard, an organization needs to plan and implement actions to address risks and opportunities. Addressing both risks and opportunities establishes a basis for increasing the effectiveness of the quality management system, achieving improved results, and preventing negative effects.” (0.3.3)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
- Looking for operational risks is everyone’s responsibility and affects every company process.
- Operational risk management allows for better planning and improved results.
- Risk assessment is required for operational activities such as product requirements review, contract negotiations, operations management, design and development, purchasing, work transfer, etc.
-
-
What is the Context of the Organization?
Every company is influenced by both internal and external factors. The ISO 9001 standard requires organizations to evaluate all the ways in which their actions and deliverables influence their stakeholders by examining the web of connectedness that determine how decisions are made in the pursuit of growth and success.

How the ISO 9001 standard applies to each business is based on the context of that specific organization, helping to define exactly how the QMS should be developed and implemented so that it directly impacts business needs and goals.
What’s Required?
“The organization shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose and its strategic direction and that affect its ability to achieve the intended result(s) of its quality management system. “The organization shall monitor and review information about these external and internal issues.” (4.1)
Things to Remember
Defining the context of your organization will require a wide-reaching evaluation of all the ways your business is impacted by both internal and external factors:
-
-
-
-
-
- Internal factors include: company culture and size, objectives and goals, product or process complexity
- External factors include: customers and markets served, communities, industry trends, technology, regulations and requirements, and the greater economy
-
-
-
-
Companies must define the relevant interested parties and determine their response to each:
-
-
-
-
-
- Employees, unions, management > labor laws, company culture, safety
- Customers and partners > contractual agreements, service expectations, requirements
- Owners, shareholders > applicable laws, expectations
- Suppliers > contractual agreements, good-faith business practices, professional courtesy
- Authorities > regulations
- Certification bodies > standards
-
-
-
-
The scope of the QMS may or may not include the entirety of the business. It is intended to define the boundaries and applicability of the QMS, and outline what will and will not be included in the system’s requirements.
Why does Leadership need to be involved in ISO 9001 Certification?
Management involvement is crucial to the success of your QMS development and implementation. Through a series of required leadership meetings, the top executives at your company will drive the initiative from the top down. They must take full, hands-on ownership for the success of the standard certification and create a priority in the organization to adhere to processes, procedures, and requirements.
What’s Required?
“Top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to the quality management system… Top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to customer focus…” (5.1.1, 5.1.2)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
- Leadership is responsible for creating the quality policy – the document that communicates the importance of meeting high quality standards.
- Top management must define measurable quality objectives and KPIs for each process in order to provide benchmarks for improvement.
- Roles, responsibilities, and authority need to be assigned appropriately to allow for delegation of tasks, decision-making, and accountability.
- Routine management, process, and document reviews are necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the system.
- Leadership is responsible for providing adequate resources to support the QMS, including workforce, equipment, infrastructure, and environment.
-
-
Planning as Part of the 9001 Certification
Planning to implement a new system into your business requires careful thought. Leadership must take the identified risks and develop structured and measurable quality objectives to address each one based on the risk management evaluations held early in the QMS development process. Additionally, companies must plan for any changes to the QMS to reevaluate potential consequences and to continuously work toward constant improvement.

What’s Required?
“When planning for the quality management system, the organization shall consider the issues referred to in 4.1 (context) and the requirements referred to in 4.2 (expectations of interested parties) and determine the risks and opportunities that need to be addressed… The organization shall establish quality objectives at relevant functions, levels, and processes needed for the quality management system.” (6.1.1, 6.2.1)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
- All actions should be proportionate to the risk they address and the impact that risk may have on product service or conformity.
- All planning should be results-driven.
- Planning is handled by managers and process owners on an ongoing basis.
- Details of all actions, including tasks to be completed, needed resources, responsibilities, dates for completion, and evaluation of effectiveness must be documented.
-
-
Support & Resources
As mentioned before, the leadership team is responsible for ensuring that the proper resources and support are in place to provide a solid foundation on which to build and implement an effective QMS. This includes equipment and facilities that result in an effective work environment, up-to-date process documentation, and a sufficient workforce. Further, all equipment must be well-maintained and kept in order with regulations for function to ensure accuracy, proper calibration, safety, and producing the desired results.
What are the Support and Resources Requirements for ISO 9001?
“The organization shall determine and provide the resources needed for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of the quality management system.” (7.1.1)
Things to Remember
People, competence, and knowledge
-
-
-
- Provide sufficient human resources and ensure needed levels of competency through training and documentation.
- Identify and maintain knowledge required by the business.
-
-
Awareness and communication
-
-
-
- Establish effective methods for communication to ensure employee awareness of and involvement in the QMS
-
-
Control of documents and records
-
-
-
- Control documented information that affects the QMS, including product quality and safety.
- Communicate changes in relevant documentation as needed.
-
-
Infrastructure and work environment
-
-
-
- Maintain needed infrastructure such as facilities, equipment, transportation resources, and technology.
- Provide a suitable working environment for people, processes, equipment, and materials.
- Identify, maintain, and calibrate equipment used to monitor and measure process results
-
-
Customer Focus
The quality of the organization’s deliverables must meet the expectations of the customer. This is the ultimate test of your QMS – ensuring customer satisfaction and keeping their needs at the forefront of your focus.
The entirety of the QMS must be geared toward customer needs and centered on the understanding of their requirements. Each plan and process should have the ultimate goal of pleasing the customer and the entire organization should ensure that all actions are rooted in the same.

Open communication is key to success, as are the careful monitoring and measurement of quality levels and customer satisfaction.
What’s Required?
“The organization shall monitor customers’ perceptions of the degree to which their needs and expectations have been fulfilled. The organization shall determine the methods for obtaining, monitoring, and reviewing this information.” (9.1.2)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
- Customer satisfaction starts with understanding their needs and requirements.
- Your QMS should address customer, statutory, and regulatory requirements.
- The entire workforce is responsible for keeping the focus of the QMS on customer satisfaction.
- All planning, objectives, operational processes, and communication procedures should support customer satisfaction.
- Processes should be established to protect customers from receiving nonconforming outputs.
- Specific objectives for product quality and on-time delivery are required.
- All feedback from customers should be utilized to determine customer satisfaction and to provide guidance on action items for improvement.
-
-
Operations Control
Operations is a blanket term covering all the activities that go into the creation of a product or service, from customer requirement review to post-shipment activities. Controls in the ISO 9001 Standard include requirements for products and services, design and development, external processes, products, and services, production and service provision, release of products and services, and control of nonconforming outputs.
What’s Required?
“The organization shall plan, implement, and control the processes (see 4.4) needed to meet the requirements for the provision of products and services, and to implement the actions determined in Clause 6… The output of this planning shall be suitable for the organization’s operations. “The organization shall control planned changes and review the consequences of unintended changes, taking action to mitigate any adverse effects, as necessary. “The organization shall ensure that outsourced processes are controlled (see 8.4).” (8.1)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
- Controls are far-reaching in the QMS and must be carefully determined to affect each step of the production process.
- If design and development are part of the company’s processes, special attention must be paid to the stages of design and resulting intellectual property.
- Controls must help ensure that desired results are being achieved.
- Controls work to ensure that externally provided resources, products, and services meet the needed requirement to uphold quality.
- Controls should be put in place to protect processes from error.
- Release of products and services should be carefully controlled to ensure that only top-quality deliverables are received by the customer.
-
-
Key Business Processes
Each process within your business that impacts the product life cycle must be controlled and improved. They are dependent on your specific organization and upon the nature of the product and/or service you provide.
What’s Required?
“The organization shall establish, implement, and maintain a design and development process that is appropriate to ensure the subsequent provision of products and services.” (8.3.1)
Things to Remember
Design and development
-
-
-
- Control product development steps including planning, reviews, verification, and validation.
- Ensure product changes are managed effectively.
- Consider part/material obsolescence.
-
-
Control of external providers
-
-
-
- Ensure adequacy of requirements communicated to suppliers.
- Verify compliance of purchased products.
- Monitor and evaluate supplier performance.
- Manage risks associated with external providers.
-
-
Production, service provision, inspection, and release
-
-
-
- Ensure proper planning and preparation of manufacturing/service provision.
- Conduct inspections and control quality.
- Control the release and delivery of products to customers.
- Manage production/service delivery transactions to ensure on-time delivery within acceptable levels of risk and resource constraints.
-
-
Post-delivery support
-
-
-
- Provide customer assistance and product support according to requirements.
-
-
Performance Evaluation & Improvement
The overall goal of the ISO 9001 process is to develop a QMS that is long-standing and helps your business progress far into the future. To create such a system, you must constantly monitor, evaluate, and improve your activities, and work to remain compliant with ISO requirements. The effectiveness and maintenance of your system must receive constant attention from all members of your team, and your top management should focus efforts on routine attention for improvement processes.

What’s Required?
“The organization shall determine and select opportunities for improvement and implement any necessary actions to meet customer requirements and enhance customer satisfaction.” (10.1)
Things to Remember
-
-
-
-
- Creating and implementing careful processes to monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate your processes will help to ensure you are meeting operational goals and KPIs, and that you comply with ISO requirements.
- Regular management reviews help maintain QMS effectiveness and alignment with strategic direction by focusing on improvement and addressing issues with inputs and outputs.
- Trained, qualified internal auditors help to ensure compliance of your QMS to ISO standards, both before your first audit and to maintain certification.
- Processes are required to handle all nonconforming outputs and nonconformities (defective products/services) through a series of corrective actions to address the root cause.
- Focus on implementing new system processes and protocols that work toward continual improvement and system innovation.
- All information related to customer satisfaction should be monitored and evaluated including quality, delivery performance, customer complaints, and requests for corrective action.
-
-
-
If you are interested in pursuing certification, contact Core Business Solutions at 866.354.0300 to talk to an ISO 9001 consultant.