Comparison of CMMI and ISO 9001
In the landscape of quality management, two prominent frameworks stand out: CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) and ISO 9001. While both aim to enhance organizational performance and quality, they do so in distinct ways. ISO 9001, an internationally recognized standard, delineates the criteria for establishing and refining a Quality Management System (QMS), fostering a culture of continual improvement and customer satisfaction. Meanwhile, CMMI offers a comprehensive model of best practices, guiding businesses in improving their key processes across various domains. In this comparative analysis, we delve into the similarities, differences, and synergies between CMMI and ISO 9001, exploring how organizations leverage these frameworks to drive excellence and innovation in their operations.
What is ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized standard that sets out the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). It provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their quality management processes and procedures.
ISO 9001 is universal and applicable to any organization regardless of its type and size or the products and services it provides.

How do Organizations Use ISO 9001?
Organizations use ISO 9001 certification as a strategic tool to enhance their quality management systems (QMS) and demonstrate their commitment to quality to customers, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies.
Here’s how organizations typically utilize ISO 9001 certification:
Establishing a Quality Management System (QMS):
ISO 9001 provides a framework for organizations to establish and implement a robust QMS. This system encompasses policies, processes, procedures, and resources needed to achieve quality objectives and meet customer requirements.
Process Improvement:
ISO 9001 encourages organizations to continuously improve their processes by identifying inefficiencies, addressing non-conformities, and implementing corrective and preventive actions. By adhering to ISO 9001 standards, organizations can streamline operations, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency.
Meeting Customer Expectations:
ISO 9001 emphasizes customer focus and satisfaction. Organizations use the principles outlined in the standard to understand customer needs, monitor feedback, and consistently deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. This helps in building trust and loyalty among customers.
Enhancing Organizational Reputation:
ISO 9001 certification is internationally recognized and respected. Organizations leverage this certification to enhance their reputation in the marketplace, differentiate themselves from competitors, and gain a competitive edge. It serves as a signal of quality and reliability to customers and stakeholders.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements:
ISO 9001 certification demonstrates compliance with relevant statutory and regulatory requirements. By adhering to the standard’s guidelines, organizations ensure that their products and services meet legal obligations and industry standards.
Facilitating International Trade:
ISO 9001 certification is often a requirement for participating in global supply chains and accessing international markets. Organizations seek certification to demonstrate their ability to consistently deliver high-quality products and services, thus facilitating trade relationships with partners worldwide.
Internal Auditing and Training:
ISO 9001 certification involves regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of the QMS and identify areas for improvement. Organizations conduct training programs to educate employees about quality management principles, procedures, and their roles in achieving quality objectives.
Continuous Improvement and Maintenance:
ISO 9001 certification is not a one-time achievement but a continuous journey. Organizations regularly review and update their QMS to adapt to changing business environments, technological advancements, and customer needs. They undergo periodic external audits to maintain certification status.
By leveraging ISO 9001 certification, organizations can systematically improve their processes, enhance customer satisfaction, mitigate risks, and drive sustainable business growth. It serves as a foundation for achieving operational excellence and fostering a culture of quality within the organization.
What is a QMS?
A QMS, or Quality Management System, is a structured framework implemented by organizations to manage and improve the quality of their products or services. It involves policies, processes, procedures, and resources aimed at meeting customer requirements, enhancing satisfaction, and achieving organizational objectives.

What is CMMI?
CMMI is an integrated model of best practices that enable businesses to improve the performance of their key business processes.
What is the CMMI Model?
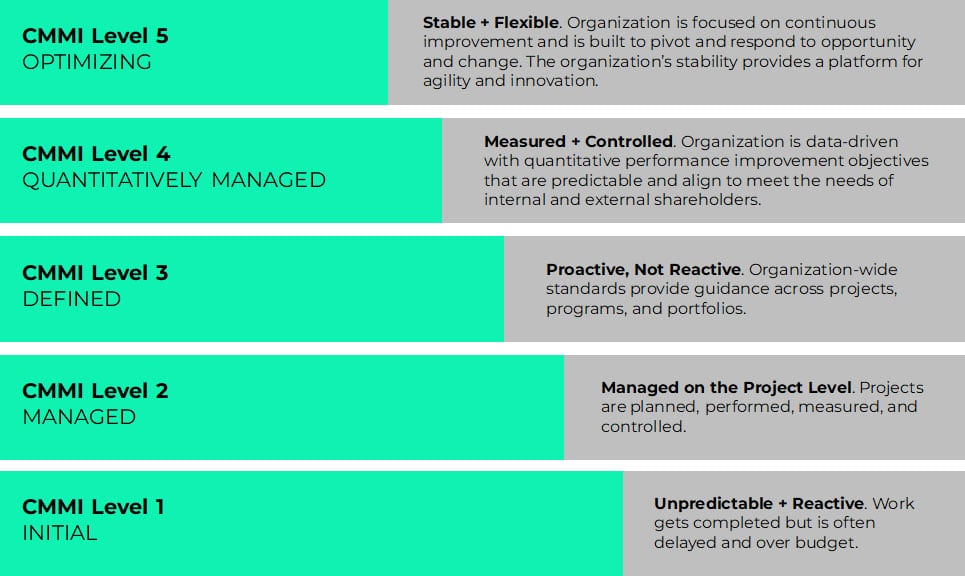
Unlike ISO 9001, CMMI has both Capability and Maturity levels. CMMI has 4 levels ranging from 0 to 3 and the 6 Maturity levels range from 0 to 5.
What are the CMMI Capability Levels?
According to https://cmmiinstitute.com/learning/appraisals/levels:
The Capability Levels of CMMI
“Capability levels apply to an organization’s performance and process improvement achievements in individual practice areas. Within practice areas, the practices are organized into practice groups labeled Level 0 to Level 3 which provide an evolutionary path to performance improvement. Each level builds on the previous levels by adding new functionality or rigor resulting in increased capability.”
What are the Maturity Levels of CMMI?
The Maturity Levels of CMMI
“Maturity levels represent a staged path for an organization’s performance and process improvement efforts based on predefined sets of practice areas. Within each maturity level, the predefined set of PAs also provides a path to performance improvement. Each maturity level builds on the previous maturity levels by adding new functionality or rigor.”
The Maturity Level Journey
Initially, every company begins its journey with CMMI at Maturity Level 1 (ML1), indicating a stage of immaturity characterized by ad hoc chaos. While most companies typically operate at Maturity Level 2 (ML2), only a few actively pursue an official rating at this level. Most companies aspire to achieve Maturity Level 3 (ML3) upon entering the CMMI framework, with some aiming even higher at Maturity Level 4. Attaining Maturity Level 5 is considered a formidable feat, representing an “excellence model” that demands exceptional effort and dedication.
How are CMMI and ISO 9001 Similar?
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) and ISO 9001 share several similarities:
Focus on Quality Management:
Both CMMI and ISO 9001 emphasize the importance of quality management within organizations. They provide frameworks and guidelines to help organizations establish effective quality management systems.
Process Orientation:
Both CMMI and ISO 9001 are process-oriented approaches. They encourage organizations to define, document, and optimize their processes to ensure consistent delivery of products or services that meet customer requirements.
Continuous Improvement:
Both models advocate for continuous improvement. CMMI promotes maturity levels and capability levels that organizations can strive to achieve incrementally, while ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of continual improvement as a fundamental principle.
Customer Focus:
Both CMMI and ISO 9001 prioritize customer satisfaction and meeting customer expectations. They emphasize the need for organizations to understand customer needs, monitor feedback, and strive to deliver products or services that fulfill those requirements.
Internationally Recognized:
Both CMMI and ISO 9001 are internationally recognized standards. They provide organizations with a common language and framework for quality management that can be understood and implemented across different industries and countries.
Certification and Appraisal:
Organizations can seek certification or appraisal against both CMMI and ISO 9001 standards. Certification demonstrates compliance with the respective standards and may be required by customers, regulatory bodies, or as part of contractual agreements.
Despite these similarities, it’s important to note that CMMI and ISO 9001 also have differences in their focus, scope, and application. While ISO 9001 primarily focuses on quality management systems, CMMI encompasses broader organizational capabilities, including software development, engineering, and service delivery. Additionally, CMMI provides a maturity model with maturity levels, whereas ISO 9001 offers a standard with requirements for a quality management system.

How are CMMI and ISO 9001 Different?
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) and ISO 9001 differ in several key aspects:
Scope and Focus:
CMMI: CMMI is a comprehensive framework that encompasses various domains such as software engineering, systems engineering, project management, and services. It focuses on improving organizational processes and capabilities to deliver high-quality products and services.
ISO 9001: ISO 9001 is a quality management standard that specifically addresses the requirements for implementing a quality management system (QMS) within an organization. While it emphasizes quality management principles, it does not prescribe specific processes or practices for other domains like CMMI does.
Structure:
CMMI: CMMI provides a maturity model structure with maturity levels (e.g., Initial, Managed, Defined, Quantitatively Managed, Optimizing) and process areas (e.g., Requirements Management, Project Planning, Measurement, and Analysis) that organizations can use to assess and improve their processes.
ISO 9001: ISO 9001 is structured around a set of clauses that outline the requirements for establishing and maintaining a QMS. These clauses cover areas such as the context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement.
Applicability:
CMMI: CMMI is widely used in industries such as software development, aerospace, defense, and information technology, where process improvement and maturity are critical for success.
ISO 9001: ISO 9001 applies to organizations across various industries and sectors, including manufacturing, services, healthcare, automotive, and more. It is recognized as a generic standard for quality management and can be implemented by organizations of any size or type.
Certification Process:
CMMI: CMMI certification involves a formal appraisal process conducted by certified lead appraisers. Organizations can achieve maturity level ratings based on their process capabilities, ranging from Level 1 (Initial) to Level 5 (Optimizing).
ISO 9001: ISO 9001 certification involves a third-party audit of the organization’s QMS against the requirements of the standard. Organizations can become ISO 9001 certified upon demonstrating compliance with the standard’s requirements.
Emphasis on Process Improvement:
CMMI: CMMI places a strong emphasis on continuous process improvement and organizational maturity. It provides a roadmap for organizations to incrementally enhance their processes and capabilities over time.
ISO 9001: While ISO 9001 encourages continual improvement as a fundamental principle, its primary focus is on ensuring that organizations establish and maintain effective quality management systems to meet customer requirements and enhance satisfaction.
While both CMMI and ISO 9001 aim to improve organizational performance and quality, they differ in their scope, structure, applicability, certification process, and emphasis on process improvement. Organizations may choose to adopt one or both standards based on their specific needs, industry requirements, and strategic objectives.

Why Implement both CMMI and ISO 9001?
“Although ISO 9001 requirements state: Consistently meeting requirements and addressing future needs and expectations poses a challenge for organizations in an increasingly dynamic and complex environment.
To achieve this objective, the organization might find it necessary to adopt various forms of improvement in addition to correction and continual improvement.”
Reference: http://www.iso.org/iso/home/store/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=62085
The CMMI model offers a pathway for ongoing performance enhancement and the adoption of best practices essential for optimizing a company’s QMS and driving overall excellence. It surpasses mere compliance requirements, fostering a culture of continual improvement and innovation.

How do CMMI and ISO 9001 Work together?
CMMI and ISO 9001 can work together synergistically to enhance organizational performance and quality management practices.
CMMI can complement ISO 9001
Firstly, CMMI can complement ISO 9001 by providing additional guidance and practices to support its implementation. For instance, CMMI practices can help organizations better understand their current capabilities and performance levels, aligning them with the requirements of ISO 9001. By leveraging CMMI, businesses can assess whether their QMS is effectively meeting their needs and objectives, thereby facilitating compliance with ISO 9001 standards.
CMMI Offers a Structural Approach to Process Improvement and Optimization
In addition, the CMMI model offers a structured approach to process improvement and optimization. By adopting CMMI practices, organizations can identify areas for enhancement within their QMS and implement targeted improvement initiatives. These initiatives not only align with the principles of ISO 9001 but also go beyond mere compliance, driving continuous performance improvement and elevating overall organizational effectiveness.
CMMI Practices can Serve as a Guide
Furthermore, CMMI practices can serve as a guide for implementing ISO 9001 requirements more efficiently and effectively. By leveraging CMMI’s framework, organizations can streamline their quality management processes, enhance process maturity, and achieve greater levels of performance excellence. This integrated approach enables organizations to not only meet ISO 9001 standards but also derive maximum value from their quality management efforts.
In Conclusion
The comparison between CMMI and ISO 9001 reveals both the diversity and synergy within the realm of quality management. While ISO 9001 emphasizes the establishment of robust QMS to meet customer requirements and enhance organizational reputation, CMMI offers a structured approach to process improvement across diverse domains. Despite their differences, organizations can harness the complementary strengths of both frameworks to propel themselves toward operational excellence. By integrating CMMI practices with ISO 9001 standards, businesses can navigate the complexities of quality management with agility and efficacy, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business landscape.
How Core Can Help
At Core Business Solutions, we understand the needs and priorities of small businesses. We’ve been there. Our expert consultants bring hands-on experience to the table. We’ve also seen how both ISO 9001 and CMMI can drive lasting improvement in your company.
Our proven process combines expert consulting, web-based tools, and online training to help you achieve success. A designated consultant will walk alongside you through every step of preparation for your ISO 9001 audit or CMMI appraisal.
You don’t need to face the audit or appraisal process alone. Let us handle the stress so you can focus on your business. When you work with our experts who know small businesses, you can get the most out of your appraisal.
Talk to a consultant today. Give us a call at 866.354.0300 or contact us for a free quote.
About Scott Dawson
Since 2010, Scott Dawson, President of Core Business Solutions, has been an active voting member of the U.S. Technical Advisory Group (TAG) to ISO Technical Committee 176 (TC 176). TAG 176 members meet to discuss and develop U.S. positions for Quality Management standards, including ISO 9001:2015, which will be revised in 2026.




