ISO 27001:2022
The latest version of ISO 27001 has arrived. Published on October 25, 2022, the new version (ISO 27001:2022) brings important updates to the standard. Initial ISO 27001 audits starting November 1, 2023, will be conducted to the 2022 standard. If you are already ISO 27001 certified, there will be a three-year transition period to update to the new revision ending on October 31, 2025. What has changed and what does it mean for your business?
What is ISO 27001?
Before we begin, here’s a quick refresher on the background of ISO 27001. If you’re already familiar with the existing standard, feel free to skip down to the next section and read about the updates.
ISO 27001 sometimes referred to as ISO27001, is an Information Security Management System (ISMS) standard. It sets internationally-accepted best practices for information security, to help you protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your information. Cybersecurity plays a major role in the standard, but the requirements also deal with the protection of physical information assets.
In today’s digital world, information security matters more than ever. Customers want to know their information will stay secure. It only takes one security breach to destroy a company’s reputation. By helping you protect your information, ISO 27001 helps you protect your brand and your customers.

To do this, it employs a set of security controls found in Annex A of the standard. That’s where you’ll find the biggest updates to ISO 27001. Annex A contains a brief overview of the security controls, but you can find more detail in the additional ISO 27002 reference standard.
What Has Changed In ISO 27001?
The previous version of ISO 27001 was released in 2013. But the world has changed since then. Information security threats have grown more complex. Our methods for preventing them need to match.
Earlier in 2022, ISO 27002 (the source of ISO 27001’s security controls) received its 2022 revision. Now, the ISO 27001 requirements have been updated to match.
The New Version Contains 93 Controls
ISO 27001:2013 contained 114 security controls. The new version contains 93 controls. Some of the previous controls have been removed. Others have been merged. Others are completely new, designed to help organizations like yours face the changing world of security threats.
The 11 Newly Added Security Controls:
• Threat intelligence
• Information security for the use of cloud services
• ICT readiness for business continuity
• Physical security monitoring
• Configuration management
• Information deletion
• Data masking
• Data leakage prevention
• Monitoring activities
• Web filtering
• Secure coding

Four Control Groups
ISO 27001:2022 organizes its controls into four control groups. A note of clarification before we dive deeper: These control groups receive their numbering from the ISO 27002 standard. As such, they are numbered 5-8. So don’t worry. You’re not missing groups 1-4, it’s just a quirk of the numbering system.
The Control Groups are Organized as Follows:
5. Organizational Controls
This group, the largest of the four, contains 37 controls. These controls deal with your organization and its processes. Among them, you will find controls such as the return of assets.
6. People Controls
This group contains 8 controls dealing with the people in your organization and the way they interact with your information. It includes controls such as information security awareness training.
7. Physical Controls
This group contains 14 controls to address the physical aspects of information security, such as facility access and printed information. It features controls such as the clear desk and clear screen policy.
8. Technological Controls
This group contains 34 controls, and it requires more technical expertise than the other groups. It deals with the cybersecurity aspect of information security, and it contains controls such as protection against malware.
Remember: Not every organization needs to meet every control. You choose the controls that apply to you. If you believe a control doesn’t apply to you, you’ll need to explain your reasoning in a statement of applicability.
Lastly, the updated standard provides attributes to help you organize and prioritize the controls.
These Five Attributes are:
• Control type
• Cybersecurity concept
• Information security properties
• Operational capabilities
• Security domains
Keep in mind: Because of all this renumbering and reorganization, you will likely need to update the labeling of your documents, even if the actual security controls you employ haven’t changed.
In addition to these changes, there are a few minor changes to some clauses to align the standard to Annex SL (the high-level structure for the ISO standards).
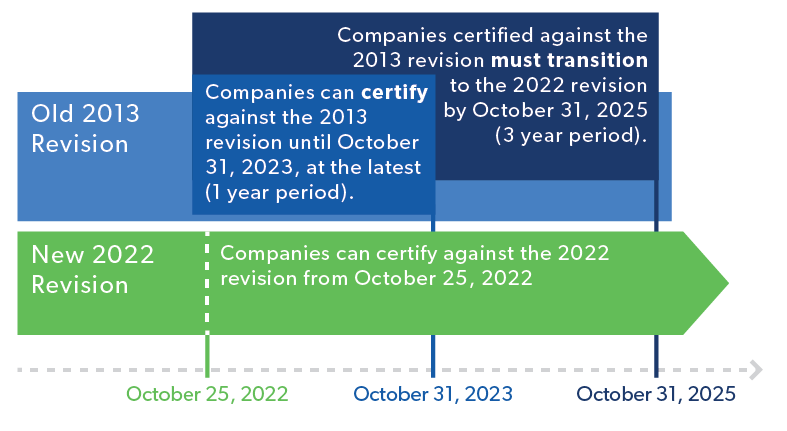
The ISO 27001:2022 Transition Timeline
As of October 25, 2022, companies can begin certifying to the updated standard. But if you’re still following ISO 27001:2013, or if you’re in the process of certifying to ISO 27001:2013, don’t panic! You have a bit more time.
You can still certify to ISO 27001:2013, until October 31, 2023. Happy Halloween! But pay attention, because some registrars might stop certifying organizations to the 2013 version before this date. If that’s the case, you may need to switch registrars or transition sooner.
The true hard deadline comes in three years, on October 31, 2025. At that point, everyone certified to ISO 27001:2013 must recertify to ISO 27001:2022. No new ISO 27001:2013 certifications will be offered at this point.
ISO 27001:2022 Transition Explained
Everyone certified to ISO 27001 will face some extra work over the next few years–even if that just means re-labeling your documents and controls. But depending on the scope of your ISMS, you might have up to 11 new controls to implement. Don’t assume this will be a quick and easy project.
It’s best to begin now. That way, you won’t be caught off guard by the upcoming changes, and you’ll have plenty of time to figure out the new technical controls.
Plus, these new controls will help your business. Cybersecurity threats are real, and they can bring down an organization overnight. The updated ISO 27001 standard can help protect your information from today’s threats.
How Core Can Help
At Core Business Solutions, we specialize in helping small businesses achieve ISO certification and information security. Our team of ISO and cybersecurity experts has real industry experience. We know what it’s like to run a small business and we know the threats and complications you face today.
Some of the new ISO 27001 controls may seem daunting. But they don’t have to be. At Core Business Solutions, we offer consulting, training, online tools, and technical solutions to make certification simple and effective.
Simply put: We take on the complicated parts of information security so you can focus on your business.
Contact us or give us a call at 866.354.0300 to learn more.
About Scott Dawson
Since 2010, Scott Dawson, President of Core Business Solutions, has been an active voting member of the U.S. Technical Advisory Group (TAG) to ISO Technical Committee 176 (TC 176). TAG 176 members meet to discuss and develop U.S. positions for Quality Management standards, including ISO 9001:2015, which will be revised in 2025.




