Please Note: The Revision of ISO 9001 has been extended to be finalized in 2026
The revision of ISO 9001, the globally recognized standard for quality management systems, is now expected to be postponed until 2026. Initially, the updated version was planned for release by the end of 2025.
In April 2024, the first draft—Committee Draft ISO 9001 (CD1)—was issued and sent to members of the ISO Technical Committee (ISO TC 176) for review. However, during the July 2024 meeting in Detroit, the committee concluded that a second draft, known as Committee Draft 2 (CD2), would be required.
This additional step was necessary because the current draft was not ready to proceed to the Draft International Standard (DIS) stage. According to an ISO committee member, there were still structural issues to resolve, and many comments needed to be addressed.
Additionally, a coordinated explanatory annex was lacking. These factors prompted the need for a second draft to ensure a comprehensive and high-quality revision of the standard.
The ISO Technical Committee 176 reconvened in September 2024 to address the remaining comments and finalize the annex structure.
Understanding the Upcoming ISO 9001 Revision
The ISO 9001 standard, a cornerstone for quality management systems (QMS) worldwide, is undergoing a significant revision to stay relevant in the digital age. This update is driven by rapid technological advancements, evolving business models, and global challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic, which have drastically altered workplace dynamics and supply chain operations. As industries face new realities, the revision aims to ensure that ISO 9001 remains practical and straightforward to implement and audit, aligning with contemporary practices and stakeholder expectations.
Expected Changes
External influences such as digitalization, remote work, sustainability, and the need for international standardization are central to this revision. Expected changes include enhancements in risk management, stakeholder engagement, and integration of digital transformation and sustainability practices.

The new standard will also strive for greater flexibility, making it easier for diverse organizations to comply, and better alignment with other management systems like ISO 14001 and ISO 45001.
Preparing for the Transition
Organizations should prepare for this transition by conducting gap analysis, updating documentation, training staff, and investing in relevant technologies. With these proactive steps, companies can ensure continued compliance, improve quality management practices, and gain strategic advantages in a rapidly changing global landscape.
Why is the ISO 9001 Standards Revision Necessary?
The digital age and evolving global landscapes demand an update to ISO 9001. Rapid technological advancements and shifting business models require an improved approach. At the same time, global challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic have profoundly altered workplace dynamics and supply chain operations, underscoring the need for resilience and adaptability in quality management.
External Influences Driving the Revision
The need to align ISO 9001 with international standards and regulations is becoming increasingly important to ensure global coherence and compliance. Additionally, evolving stakeholder expectations regarding quality, transparency, and corporate responsibility are driving revisions to meet these elevated benchmarks.

What are the Main Changes Expected in the ISO 9001:2026 Revision?
According to the ISO TC 176/SC2/WG29 report, “adjustments to ISO 9001 are planned with regard to the aspects of resilience, supply chain management, change management, sustainability, dealing with risks [and] organizational knowledge”.
The core structure of the standard will remain unchanged. The revision will simply update the previously used High-Level Structure (HLS) to the new Harmonized Structure (HS), as was done in the recent ISO/IEC 27001:2022 update.
While the details of the revision remain confidential, experts anticipate significant updates in the following key areas:
Integrating Ethics and Integrity within Leadership Practices
The revision focuses on integrating ethics and integrity within leadership practices, recognizing their foundational role in quality management.
Enhanced Focus on Risk Management
Expect a stronger emphasis on proactive strategies, including risk identification, mitigation, and adaptation to evolving threats.
Separating Risk and Opportunity
One of its potential goals is to separate risks and opportunities, offering organizations clear guidance on how to address each element individually. There is some discussion among experts that there should be more focus and guidance about opportunity going forward.
Greater Emphasis on Stakeholder Engagement
The revision will most likely seek to prioritize the perspectives of all stakeholders—customers, employees, suppliers, and the community to make sure their voices are central to the decision-making process.
Integration of Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0
With the rise of digital technologies, the new standard is likely to incorporate elements of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation. Companies will need to adapt their QMS to leverage digital tools such as AI, IoT, and big data analytics for quality management. This could involve significant investments in new technologies and training for staff.

Additionally, the revision seeks to ensure that new and revised requirements are practical for implementation and straightforward to audit.
Increased Emphasis on Sustainability and Social Responsibility
The updated standard will likely include more explicit requirements for sustainability and social responsibility. Organizations will need to demonstrate how their QMS supports environmental stewardship and social accountability. This could involve adopting greener processes, reducing waste, and ensuring ethical practices throughout the supply chain.
Greater Flexibility and Simplification
The revision aims to make the standard more adaptable to different types of organizations, regardless of size or sector. This could lead to more streamlined and simplified requirements, making it easier for smaller businesses to comply. Companies might need to revise their documentation and procedures to align with the new, more flexible guidelines.
Improved Alignment with Other Management Systems
Editorial adjustments are expected to better align the standard with other management systems, such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety), promoting greater integration and consistency across standards.
The ISO 9001:2026 revision is designed to keep the standard relevant and effective in the face of modern challenges. By proactively adapting to these changes, organizations can not only maintain compliance but also enhance their overall quality management capabilities, leading to better performance and competitive advantage.
What is the Timeline for the ISO 9001 Standards Revision?
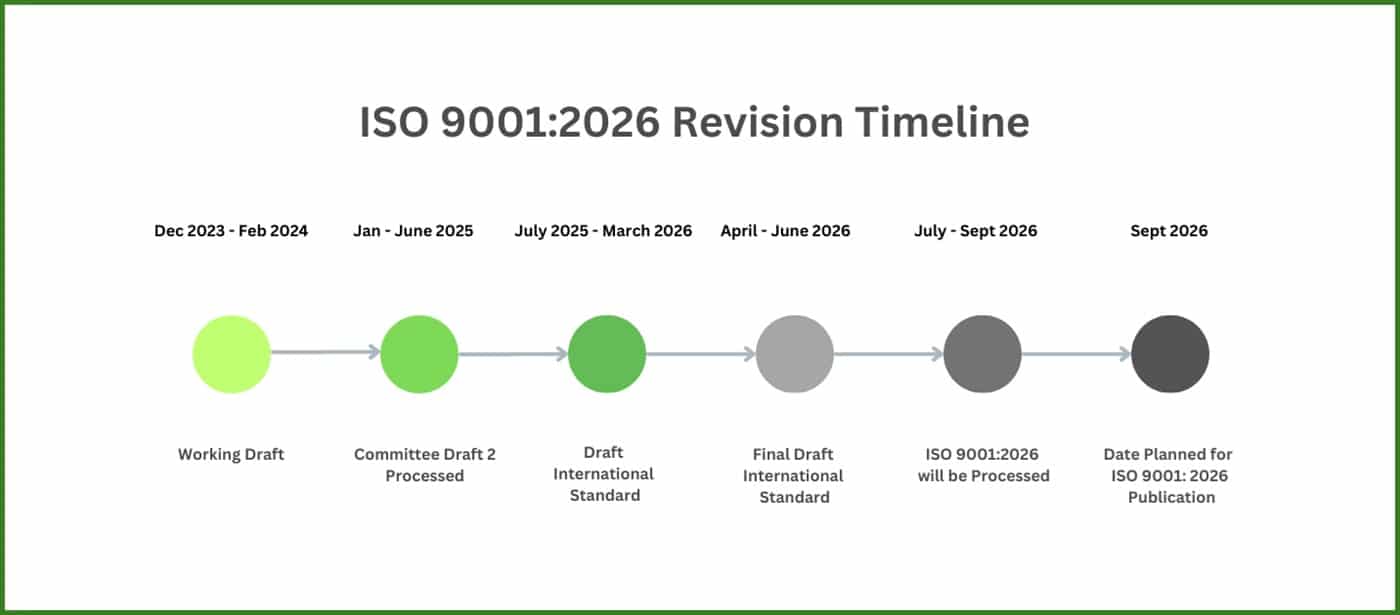
What is the Timeline for companies to Transition to ISO 9001:2026?
We don’t know yet but, when a new version of ISO 9001 is released, there is typically a transition period (usually around three years) during which organizations can update their QMS to meet the new requirements. During this period, organizations can still get certified to the 2015 version, but they will need to transition to the 2026 version by the end of the period to maintain their certification.

Organizations need to monitor updates from their certification bodies and industry authorities for specific timelines and guidance regarding the transition to ISO 9001:2026 once it is released.
How can Organizations Prepare for the Transition?
Companies should prepare for the ISO 9001:2026 revision for several important reasons. Anticipating and adapting to these changes will not only ensure compliance but also enhance their overall quality management practices, leading to numerous strategic and operational benefits.
Conducting a Gap Analysis:
Assess current QMS against the anticipated changes to identify areas needing improvement.
Training and Awareness:
Ensure that staff at all levels are aware of the upcoming changes and understand their roles in implementing them.
Updating Documentation:
Revise QMS documentation to reflect new requirements and improve clarity and simplicity.
Internal Audits:
Perform internal audits to assess readiness for the new standard.
Engaging Stakeholders:
Communicate with stakeholders about the changes and how they will be addressed in the QMS.
Investing in Technology:
Explore and invest in new technologies that can support enhanced quality management practices.
Addressing the Revision
Preparing for the ISO 9001:2026 revision is vital for ensuring continued certification, enhancing quality management practices, and leveraging the benefits of new technologies and sustainability initiatives. By proactively addressing these changes, companies can maintain compliance, improve operational efficiency, and achieve strategic business advantages.
Please Note:
ISO 9001 Climate Change Amendment
Effectively Immediately
On February 23, 2024, a new Amendment to ISO 9001 was published and it impacts all companies that are currently ISO 9001 certified as well as any certifications going forward. Learn More
About Scott Dawson
Since 2010, Scott Dawson, President of Core Business Solutions, has been an active voting member of the U.S. Technical Advisory Group (TAG) to ISO Technical Committee 176 (TC 176). TAG 176 members meet to discuss and develop U.S. positions for Quality Management standards, including ISO 9001:2015, which will be revised in 2026.




